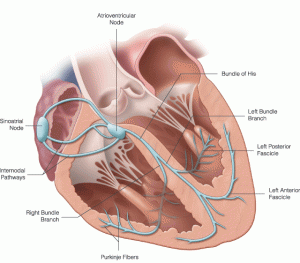
Sinus Rhythms
a. Normal Sinus Rhythm
Examples of NSR
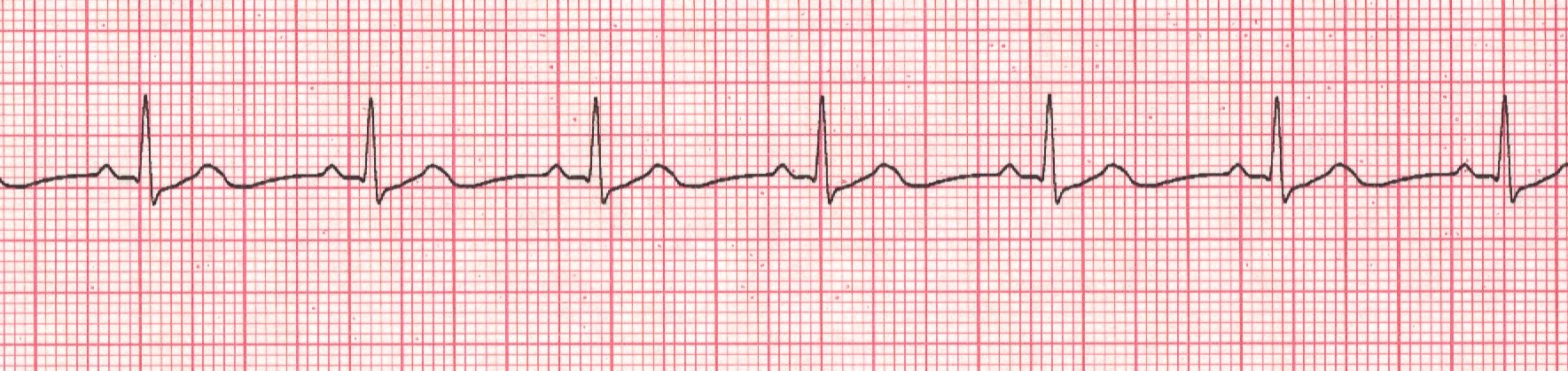
Rules:
Regular ,
60-100bpm ,
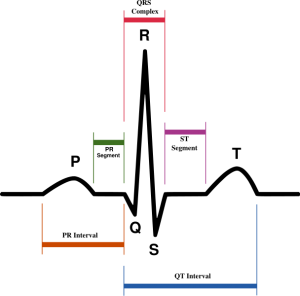
P wave is uniform, upright,
and there is one in front of every QRS ,
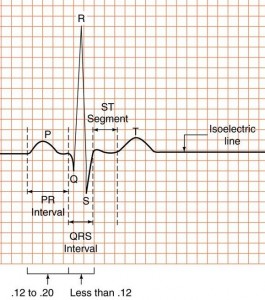
PRI is 0.12-0.20 and constant ,
QRS <0.12
Concern level: None
b. Sinus Bradycardia
Example of Sinus bradycardia
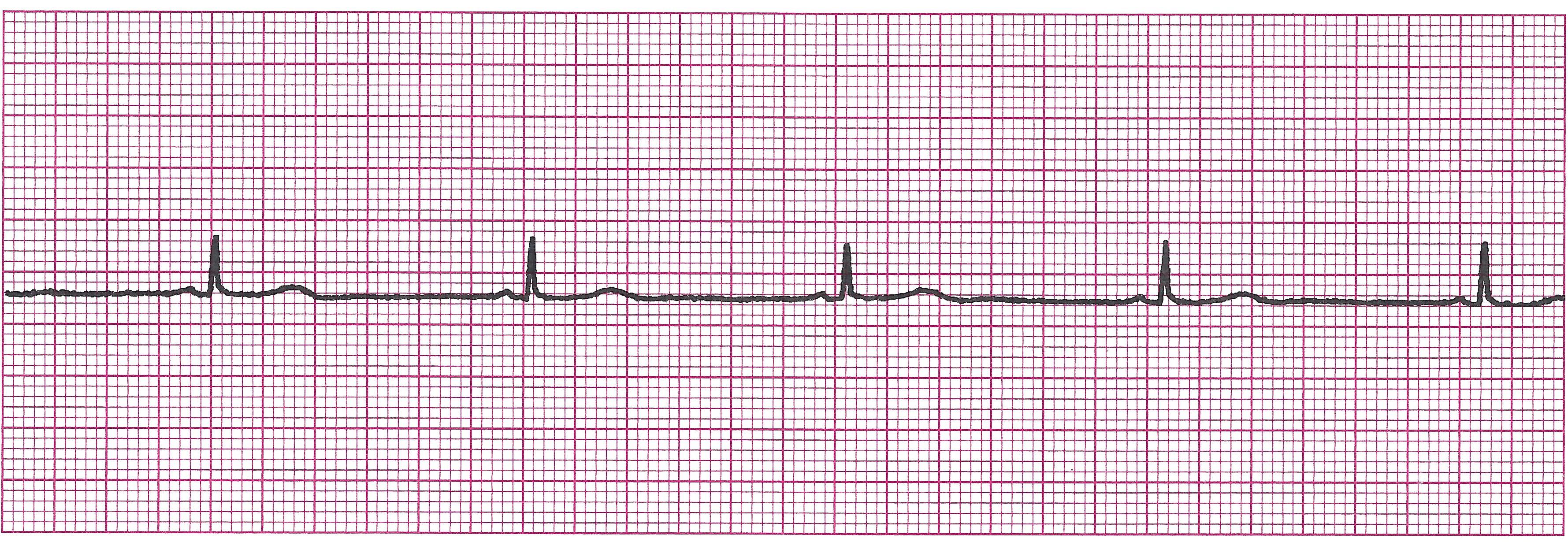
· Rules:
Regular
<60bpm
P wave uniform, upright, and one before every QRS
PRI 0.12-0.20sec and constant
QRS <0.12sec
Concern: Sometimes. Depends on clinical situation and how bradycardiac patient gets. The slower the rate, the greater the concern.
c. Sinus Tachycardia
Example of Sinus tachycardia
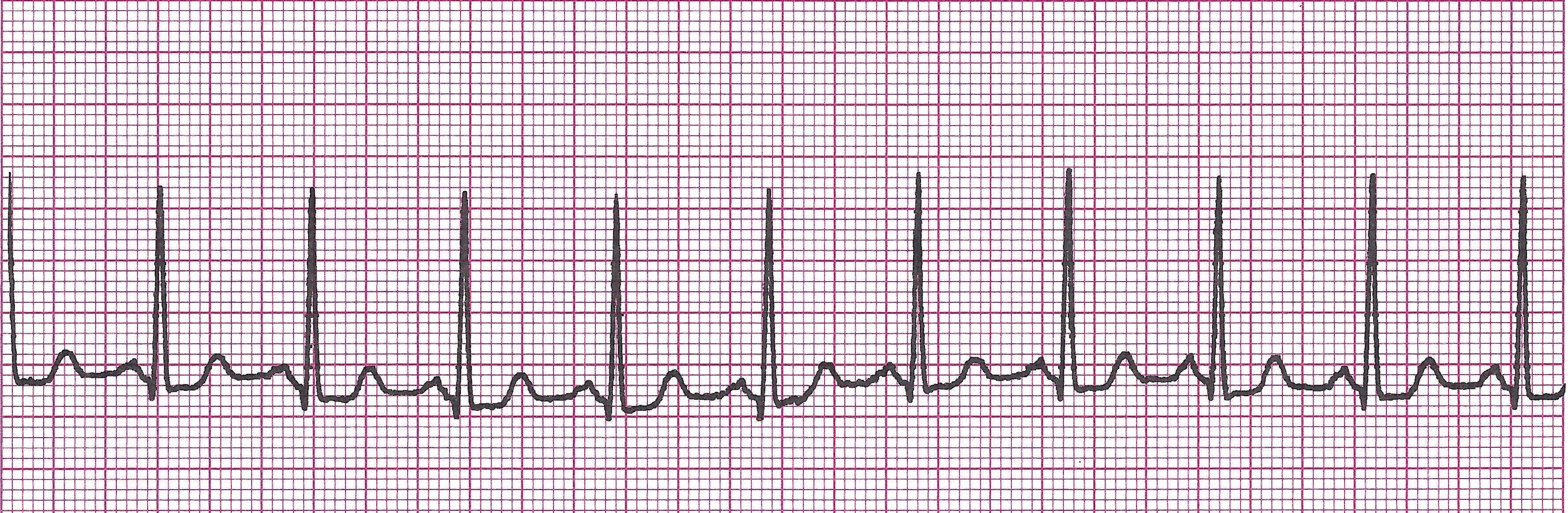
Rules:
Regular
>100bpm
P wave same as above
PRI 0.12-0.20sec, constant
QRS <0.12sec
Concern: Sometimes. Depends on clinical situation and how tachycardic patient gets. The faster the rate, the greater the concern.
d. Sinus Arrythmia
Example of Sinus Arrhythmia
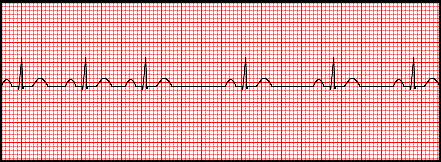
Also called “Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia”. Occurs when your heart rate cycles with your breathing. When you breathe in, your heart rate speeds up slightly. When you breathe out, your heart rate slows back down.
Rules:
R-R intervals vary; change with patient’s respirations
Rate usually 60-100bpm, but can be slower
P wave same as above
PRI 0.12-0.20sec, constant
QRS <0.12sec
Concern: Usually none
Sinus pauses and sinus arrest
Caused when the sinus node fails to generate an electrical impulse to stimulate the heart to beat. Many times both of these categories are lumped into one called “Pauses” when interpreting rhythms.
1) Sinus Pause/Sinus block
A sinus pause is followed by a delayed, next sinus beat only.
Example of Sinus pause/Sinus block
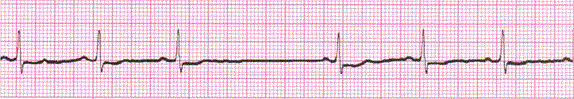
Rules:
Irregular due to pause. Pause must be followed by a sinus beat. Length of the pause is usually the same as or a multiple of the distance between two other P-P intervals.
Rate is usually normal but depends on the underlying rhythm.
P waves are uniform, upright, and before every QRS.
PRI 0.12-0.20sec, constant
QRS <0.12sec
Concern: Can be concerning. Depends on clinical situation
2) Sinus Arrest
A pause, however, many times is followed by an escape beat. This is called sinus arrest as the sinus node is taking too long to beat again needs help from the AV node. NOTE: Patients with sinus arrest may have a history of syncope, near syncope, and/or falls.
Example Sinus Arrest
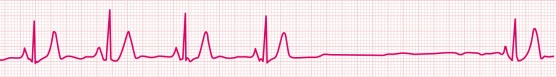
Rules:
Irregular due to pause. Pauses will vary in length and are usually more than one PQRST complex long.
Rate varies depending on underlying rhythm.
P waves uniform, upright, and one before every QRS
PRI 0.12-0.20sec, constant
QRS <0.12sec
Concern: Can be concerning. Depends on clinical situation
STOP! TIME FOR PRACTICE STRIPS ON VARIOUS SINUS RHYTHMS